Advantages and Disadvantages of LCD Display: A Comprehensive Guide

Exploring the Basics of LCD Displays
What is an LCD Display?
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a flat-panel technology. It is used in TVs, computer screens, smartphones, and more. It works by using liquid crystals to adjust light. These crystals don’t produce light themselves. They rely on a backlight or reflector. This creates color or monochrome images. The LCD display controls liquid crystal alignment. This lets or blocks light in patterns. The result is the visuals seen on the screen.
Key Features of LCD Technology
LCD technology is known for saving energy. It has a slim design. It provides clear, vivid images. Its backlight ensures even brightness. Improvements in LCD tech have brought higher resolutions. They also offer better color accuracy. Compared to OLED, LCDs cost less. They last longer. LCD screens remain the top choice in the market.
Common Applications of LCD Displays
LCDディスプレイ are versatile. They are key parts of TVs and computer monitors. They are used in smartphones, tablets, and digital cameras. They appear in car dashboards and medical devices like ultrasound machines. Their lightweight and low power use make them great for portable devices. These include laptops and handheld gaming consoles.

The Advantages of Using LCD Displays
Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
LCD displays save energy. Unlike old CRT displays, which use lots of power, LCDs need little energy. This makes them perfect for battery-powered devices. Examples are laptops and smartphones.
Lightweight and Compact Design
LCD displays are slim. They are light in weight. This has changed the device design. Manufacturers can make thinner, portable gadgets. Functionality stays intact.
Superior Image Quality and Resolution
Modern LCD displays have great image quality. They offer high resolutions like Full HD (1920×1080) or 4K Ultra HD (3840×2160). They show bright colors and sharp details. This improves user experience in many uses.
Wide Compatibility with Modern Devices
LCD screens work with most devices. They use standard interfaces like HDMI and Display Port. This allows easy connection with gadgets. These range from gaming consoles to professional cameras.
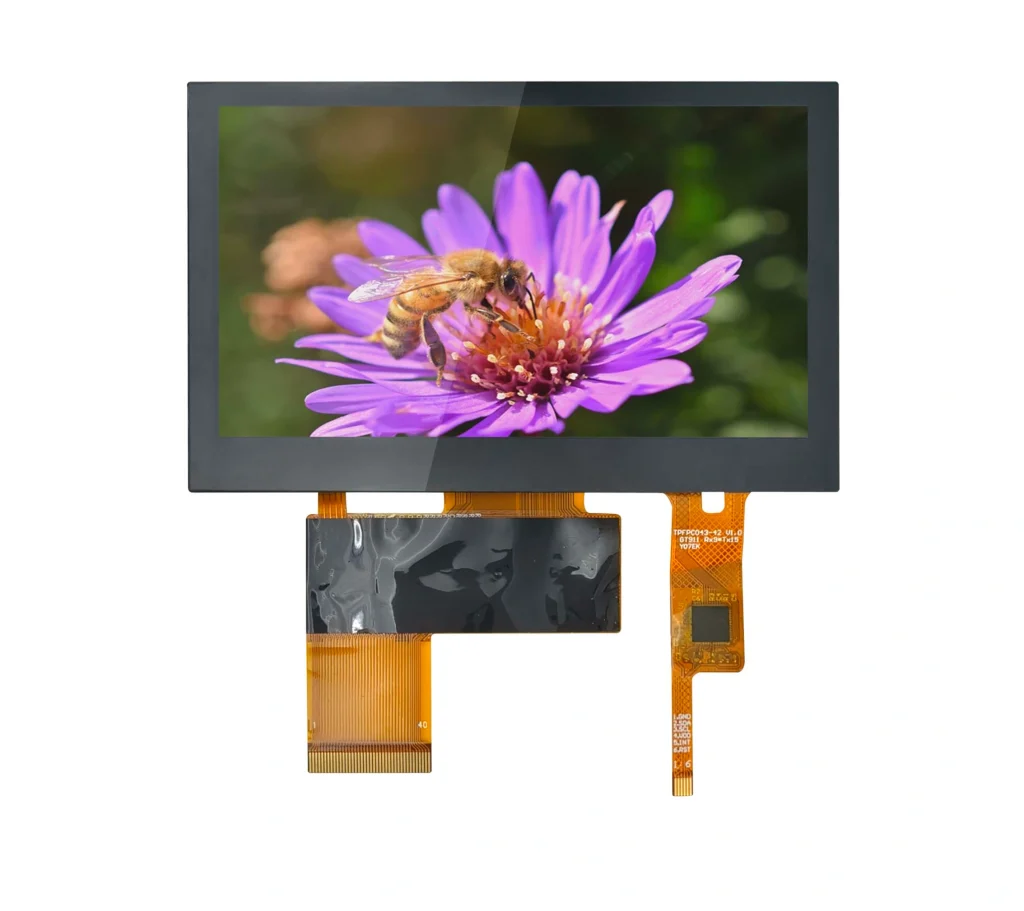

The Drawbacks of LCD Displays
Limited Viewing Angles
LCD displays have a downside. Viewing from sharp angles can distort colors. Images may look faded. IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology helps. It widens viewing angles.
Performance in Bright Environments
LCD screens can be hard to see in bright light. Direct sunlight causes glare from the backlight. Anti-reflective coatings help. Higher brightness settings also work. But these may raise costs.
Potential for Screen Burn-In or Dead Pixels
LCDs are less likely to have burn-in than OLEDs. But they can have dead pixels. These are tiny spots that don’t show images right. Over time, this affects user experience.
Comparing LCD Displays with Other Display Technologies
LCD vs. LED Displays
|
特徴 |
LCD |
LED |
|
Light Source |
Fluorescent backlight |
LED (Light Emitting Diodes) backlight |
|
エネルギー効率 |
Less efficient than LED |
More efficient due to LEDs |
|
輝度 |
Decent; struggles in very bright areas |
Brighter; better for outdoor use |
|
色の精度 |
Good colors |
Better colors and contrast |
|
耐久性 |
Long-lasting |
Longer-lasting than traditional LCDs |
|
料金 |
More budget-friendly |
Slightly pricier due to advanced tech |
LCD vs. OLED Displays
|
特徴 |
LCD |
OLED |
|
Light Emission |
Uses backlight; no direct light |
Self-emissive; pixels produce light |
|
エネルギー効率 |
Better than CRT, less than OLED |
Very efficient for dark scenes |
|
画質 |
Good colors; weaker blacks |
Great contrast with true blacks |
|
耐久性 |
Longer lifespan; less burn-in |
Shorter lifespan; prone to burn-in |
|
料金 |
Cheaper due to established production |
Costly due to complex production |
|
Eye Comfort |
Less blue light than OLED |
Higher blue light; may strain eyes |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Display Type
- Application Requirements: For industrial uses like control panels or medical devices, durability matters. Consistent performance is key. CDTech’s 15.0-inch Industrial TFT-LCD Displayis ideal here.
- Budget Constraints: If cost matters most, LCD displays are affordable. They keep essential features.
- Visual Preferences: Want vivid colors and deep blacks? OLED screens may be better. They cost more.
- Environmental Conditions: For outdoor use, brightness and sunlight visibility are vital. CDTech’s 10.1-inch High-Brightness LCD Panel is built for this.
An Overview of CDTech and Its Products
Introduction to CDTech’s Innovations in Display Technology
Commitment to Quality and Performance
cdtech leads in the display industry. It focuses on quality and performance. Its products meet varied needs. They ensure reliability in many applications.
Expertise in Advanced Display Solutions
CDTech has deep experience. It creates ソリューション with the latest advancements. These remain affordable.
Cdtechが提供するその他の製品
OLED Panels for Enhanced Visual Experience
CDTech’s OLED panels suit high-end uses. Image quality is critical here. Their self-emissive tech delivers bright colors and strong contrast.
Emerging Technologies in Display Manufacturing
CDTech explores new tech like micro-LEDs and quantum dots. It aims to offer innovative solutions. These meet future market needs.
よくある質問
Q: What makes LCD displays different from OLED?
A: LCD screens use a backlight for light. OLED screens have self-emissive pixels.
Q: Are LCD displays suitable for industrial use?
A: Yes. CDTech’s 15-inch Industrial TFT-LCD Display is made for tough settings. It offers durability.
Q: Why are OLED displays more expensive than LCDs?
A: OLEDs have complex production. This raises costs.
Q: Which type of display is better for outdoor visibility?
A: LED or high-brightness LCD panels work better in sunlight. CDTech’s 10-inch High-Brightness LCD Panel is a good example.
Q: Are there any drawbacks to using an OLED screen?
A: OLED screens last less time. They are prone to burn-in compared to LCDs.


 2025-05-08
2025-05-08  11:50
11:50 

