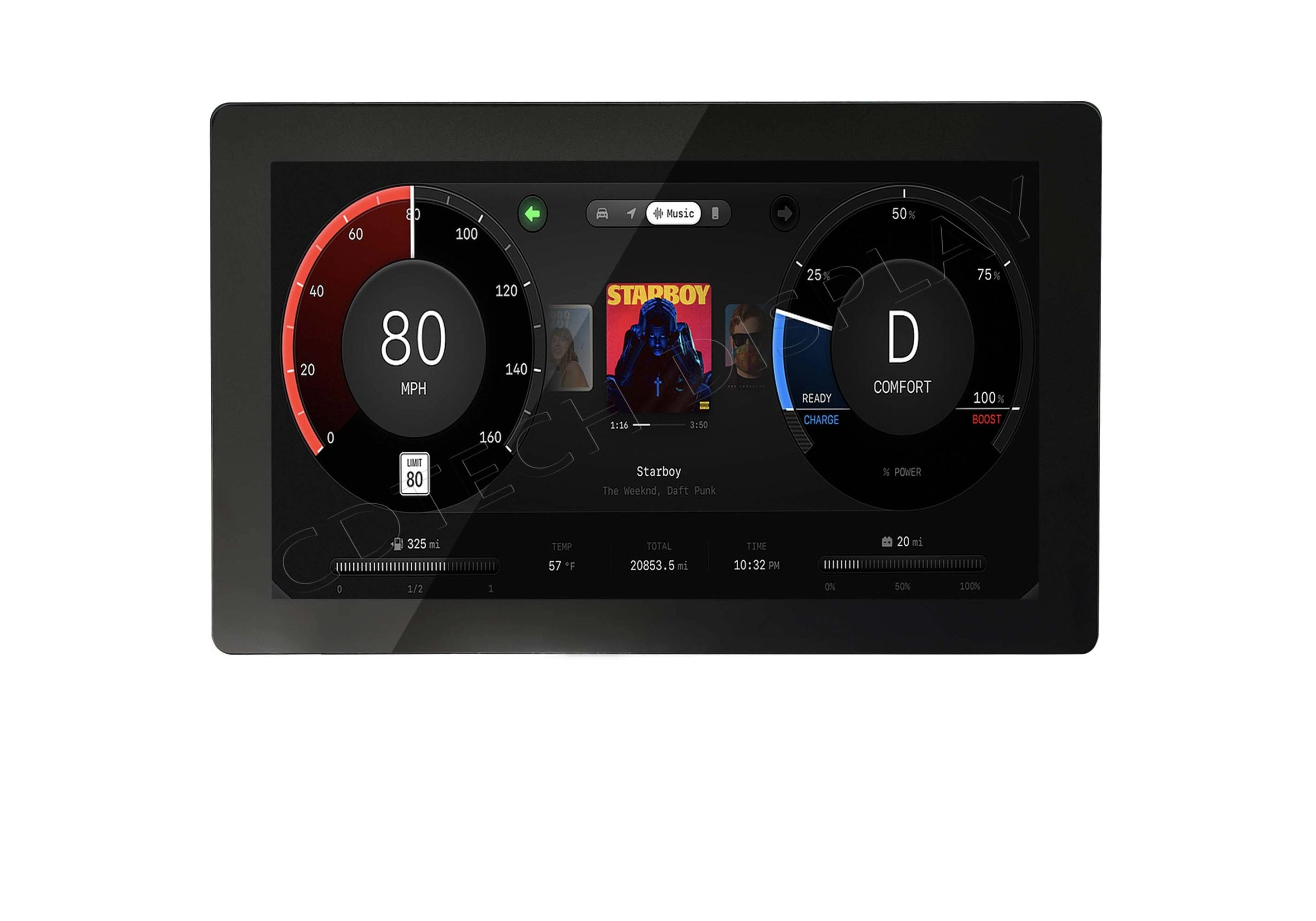
Comparing Different Types of Touch Screen Displays in the Market
What Are the Main Kinds of Touch Screen Technologies?
Touch screens are a key part of modern devices, powering everything from phones to kiosks, factory control panels and medical tools. Knowing how different touch technologies work helps you pick the right one for your needs.
How Do Resistive Touch Screens Work?
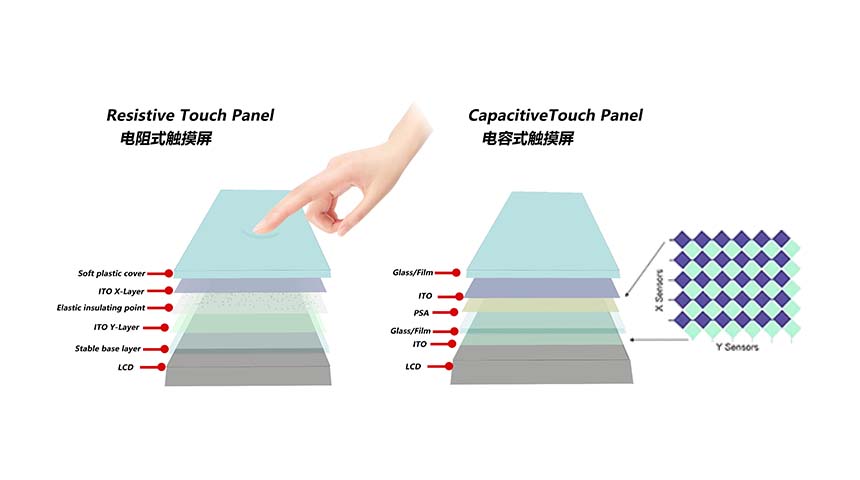
Resistive touch screens use two thin layers with a tiny gap between them. When you press the screen with a finger or stylus, the layers touch, detecting the input.
Single-Touch vs. Multi-Touch
Most resistive screens handle only one touch at a time. This works for simple tasks but isn’t great for things like pinch-to-zoom that need multiple touch points.
Pros and Cons of Resistive Technology
Resistive screens are tough and affordable. They work with gloves or styluses, perfect for industrial settings. But they’re less clear and slower to respond than capacitive screens. –With Capacitive Touch Panel or Resistive Touch Panel option..
What Is Capacitive Touch Technology?
Capacitive screens sense the electrical charge from your body to detect touch. They don’t need pressure—just a light tap with something conductive, like your finger.
Surface Capacitive vs. Projected Capacitive
Surface capacitive screens have a single conductive layer on the glass. Projected capacitive (PCAP) screens use a grid of tiny wires inside. PCAP allows multi-touch and is common in phones and tablets for its precision and speed.
Sensitivity and Durability
Capacitive screens give sharp images, quick responses and support multi-touch gestures. They cost more than resistive ones and may not work with gloves unless specially made.

How Does Infrared Touch Technology Work?
Infrared (IR) touch screens use a grid of invisible light beams created by IR emitters and sensors around the screen’s edges.
The Role of IR Emitters and Sensors
When something like a finger or stylus breaks the beams, sensors pinpoint the spot, registering the touch. Since there’s no layer over the screen, IR displays are very clear.
Benefits for Specific Uses
IR screens are great for big displays like interactive boards or public kiosks. They work with any input, including gloved hands and last long since the screen itself doesn’t wear out.
What Makes Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Touch Screens Special?
SAW technology uses sound waves that travel across the screen’s surface. A touch absorbs these waves, letting the system detect the exact spot.
How Acoustic Waves Work
Waves move across transducers at the glass edges. The system tracks changes in the wave patterns to find touch points.
Environmental Factors and Uses
SAW screens offer great image quality but can be affected by dust or water drops. They’re best for clean indoor settings like ATMs or info kiosks.
How Do These Technologies Compare in Real-World Use?
Which Touch Screen Holds Up in Tough Conditions?
In rough industrial settings with gloves or moisture, resistive screens often do better because they rely on pressure. In industrial use, touch screens are utilized in control panel systems, human-machine interfaces (HMIs) and automation systems. Infrared screens also work well outdoors but need regular cleaning to keep sensors clear.
Differences in Cost, Accuracy and Lifespan
Resistive screens are cheap but less precise and wear out faster due to physical contact. Capacitive screens are accurate and durable but pricier. IR screens balance cost and longevity if kept clean.
Power Use Across Technologies
Capacitive screens use more power due to constant scanning for multi-touch. Resistive screens use less but lack advanced features. IR screens vary in power use based on their setup.
Who Is CDTech and What Do They Offer?
CDTech’s Expertise in Touch Displays
At CDTech, we focus on making advanced TFT LCD modules with touch options like capacitive (PCAP) and resistive (RTP). TFT LCD Module. Our team works closely with clients to create solutions that fit their specific needs.
What Touch Screen Displays Does CDTech Make?
Product Range and Customization
We offer products from 3.5-inch TFTs to 10.1-inch HD modules with PCAP and RTP interfaces. Models with 1024×600 resolution IPS panels and projected capacitive touch are great for car dashboards or medical devices.
Industries Served by CDTech
Our displays support sectors like Industrial Display, Vehicle Display, Intelligent Appliance Display, meeting tough needs for reliability, sunlight readability, vibration resistance and long lifecycles.

What Should You Think About When Choosing a Touch Screen?
Is Your Use Indoors or Outdoors?
The environment matters a lot. Touch screen displays enable operators to monitor and control machinery, adjust settings and access real-time data with ease. For outdoor use with sun or water exposure, choose infrared or specially treated capacitive screens.
How Much Do Multi-Touch Features Matter?
If your project needs gestures—like retail kiosks or teaching tools—multi-touch is a must. Touch screen monitors for personal use allow users to explore website menus without using a keyboard and mouse.
What’s Your Budget and Lifespan Goal?
For low-cost projects needing basic input for short periods, resistive screens work fine. For long-term uses like healthcare or transport, capacitive screens give better value despite higher costs. Medical touch screen display specially designed for medical use enhancing data access.
FAQ
Q: What’s the difference between resistive and capacitive touch screens?
A: Resistive screens sense pressure when two layers touch; they work with gloves or styluses but only handle single-touch. Capacitive screens detect electrical changes from fingers, offering better clarity and multi-touch but may not work with non-conductive inputs unless designed for it.
Q: Which touch screen is best for industrial settings?
A: Resistive technology often wins because it works with gloves and handles dusty conditions well. In industrial use enable operators to monitor adjust settings.
Q: Can CDTech customize touch screens for specific needs?
A: Yes, we tailor solutions with size changes, interface options (PCAP/RTP), brightness levels and FPC design tweaks, based on client needs for industries like automotive or smart appliances.



 2025-09-11
2025-09-11  11:50
11:50