Comparing LCD Glass Panel Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Getting the Basics of LCD Glass Panels
What’s an LCD Glass Panel?
An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) glass panel is a key part in today’s screen tech, working as a guard layer and a look-booster. It has many layers, with the glass part usually the top lens or base. The main job of the glass panel is to protect inside bits—like liquid crystal layers and polarizers—while keeping clear and quick response.
In most screen setups, it’s key to tell apart the top glass and the real display layers below. The cover glass sits atop the LCD stack and provides surface durability, touch functionality, and improved optical performance through coatings like anti-glare or anti-reflection. Beneath it, the LCD layers manage image rendering by modulating light through liquid crystals aligned between transparent electrodes.
Key functions of a cover lens include: surface protection (scratch, impact), touch interface durability, anti-glare/anti-reflection coatings, and support for capacitive or IR touch panels.
Are LCD Panels Built from Glass?
Yep, LCD panels are usually made with glass stuff, especially as bases and top lenses. The glass in these panels plays a big role thanks to its clear optics, tough build, and fit with fancy making ways.
Glass is one of the best materials that we use in electronics to protect screens because it is very hard and it is hard to scratch. It is mechanically strong, cheap, and exceptionally good in optics. Transparency rates for display glass typically exceed 90%, ensuring minimal interference with light transmission and image quality.
While other choices like plastic are out there, they often miss the needed hardness and optic traits for pro-level screens. Plastic lacks scratch resistance and optical clarity; it’s suitable for low-cost devices but not recommended for industrial use.

Kinds of LCD Glass Panels and Their Traits
What Are the Main Kinds of Glass in LCD Screens?
Several kinds of glass go into LCD builds, each picked for what the job needs:
Soda-lime glass: Made from basic silica and soda ash, it offers low strength and is typically used in budget devices.
Tempered glass: This is thermally treated soda-lime glass with medium strength, suitable for consumer electronics.
Aluminosilicate glass: Composed of aluminum and silica, it offers high strength and is used in automotive and industrial displays.
Chemically strengthened glass: Undergoes ion-exchange treatment for very high strength, ideal for rugged and laminated modules.
Each kind differs in hardness (rated by Mohs scale), light pass, heat stand, and power to handle outside stress.
How Does Toughened Glass Boost Screen Work?
Toughened glass ups lasting power by raising surface hardness and hit stand. There are two main ways:
Thermal tempering: Glass is heated above 600°C and rapidly cooled to induce surface compression. This process results in moderate strength but can create thicker panels with edge distortion.
Chemical strengthening: A sodium-potassium ion exchange process strengthens the glass at the molecular level without adding bulk. This method allows for thinner panels with higher resilience.
With chemical strengthening we can make glass even 6 or 8 times mechanically stronger than regular one. These traits make chemically strengthened glass perfect for spots like factory terminals, outside kiosks, or medical gear where lasting and safety matter big.
Matching Optic and Tough Traits Across Panel Kinds
Which Bits Set the Lasting Power of an LCD Glass Panel?
Lasting power comes from several points:
-
Hardness: Rated using the Mohs scale.
-
Impact resistance: Assessed using IK ratings which quantify how much mechanical energy a glass panel can withstand before failing.
-
Surface treatments: Anti-glare reduces mirror-like reflections; anti-reflective coatings improve contrast outdoors; anti-fingerprint makes cleaning easier.
These traits are key in jobs where rough spots or lots of use happen.
How Do Different Glass Kinds Hit Look Quality?
The glass pick straight hits how a pic looks through the panel:
Light Transmission: For glass, the transparency rate is typically more than 90% or even 95% percent.
Color Accuracy: Low-iron glasses like Optiwhite offer better color reproduction due to reduced greenish tinge.
Reflectivity: Treated surfaces reduce glare and enhance outdoor readability.
Touch Responsiveness: Thinner chemically strengthened glasses allow better capacitive touch sensitivity without compromising protection.
Optical bonding ups look work more. Optical bonding reinforces structural integrity by eliminating air gaps—important for outdoor displays.

Common Spots for Each Kind of LCD Glass Panel
Where Do Different LCD Glass Panels Usually Go?
Factory Settings
Tough displays need better hit stand and outside seal. For special environments and extreme weather, our products can be designed with touchable by gloves, waterproof, anti-condensation, anti-shatter, anti-UV, etc.
Home Gadgets
Gear like phones or tablets like light but tough picks such as tempered or aluminosilicate glass.
Outside Digital Signs and Kiosks
These jobs want high see under sun. Laminated glasses discussed lastly highlighting advantages conferred primarily enhanced mechanical strengths alongside additional functionalities derived inserting specialized films within layered constructions offering UV/IR protection options vital outdoor deployments.
Questions About LCD Panel Stuff and Their Jobs
Why Is Chemically Toughened Glass Big in Touch Screens?
Better surface hardness ups life under lots of touch. Chemical strengthening makes sure stand against scratches from repeat finger or pen hits—making it perfect for ATMs, kiosks, or factory HMIs.
Can All Glass Kinds Work With Touch Tech?
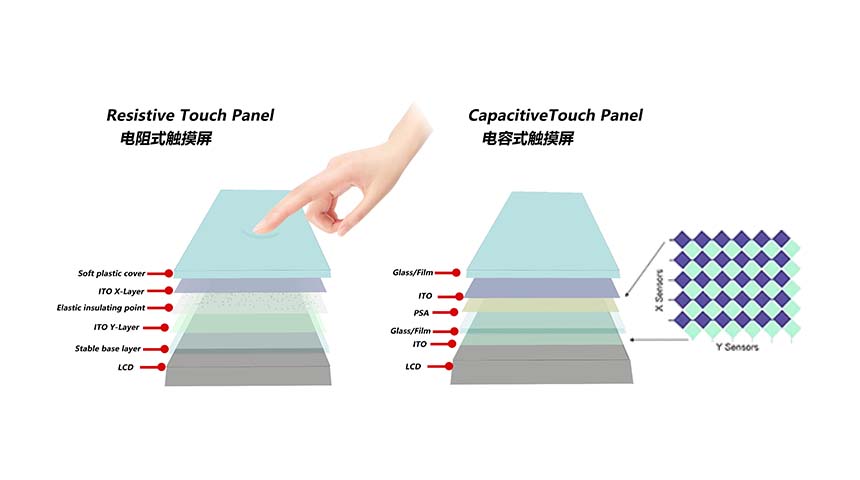
Not all glass kinds fit. Capacitive touch needs conductive layers and set thickness fits. We can also develop more derivative solutions on the standard LCD display according to customer requirements, such as custom backlight, FPC (LCD module or CTP), resistive touch panel (RTP) and projected capacitive touch panel (CTP) or anti-reflective (AR) / anti-glare (AG) / anti-fingerprint (AF) coating.
CDTech’s Spot in Top LCD Glass Panel Making
Who’s CDTech and What Makes Their LCD Panels Pop?
At CDTech, we focus on making display panels that use these top toughening ways. Shenzhen CDTech Electronics established in 2011, is a national high-tech enterprise specializing in TFT LCDs, Touch Displays, HDMI Displays and other display products. Our display solutions are designed to meet industry-specific requirements for impact resistance, longevity, and visual quality.
CDTech is turning into a world-known Display and Touch fix giver. With stable quality system control and experienced management capabilities, CDTech can provide high-quality and cost-effective products to customers in different fields around the world. We offer both standard and customized solutions built around robust quality control systems certified under ISO9001, ISO14001, ISO13485, IATF16949.
Our products can be widely used in Industrial Control Equipment, Medical, Smart-Home, Automotive and Vehicle Displays, Instrumentation, and other Information Terminal applications.
What Kinds of LCD Glass Panels Does CDTech Bring?
Chemically Toughened Top Glass Fixes
We bring top surface lasting with optional blast-proof films—especially good for medical-level or outside products.
Optical Bonding Tech Mix
Our optical bonding way cuts air gaps between layers to drop glare, up contrast, better touch feel, and stop fog.
Tweak Options for Field-Specific Needs
With customized LCD OD, LCD AA, FPC OD, backlight option. We fit display modules for set fields like transport systems or smart terminals. Our team can mix special coatings (AG/AR/AF), custom PCBs, or unique shapes based on your work spot.
FAQ
Q: Which panel is best, LCD or LED?
A: LED refers to backlighting technology used in some displays; LCD refers to the display technology itself. Many “LED” screens are actually LED-backlit LCDs. The choice depends on brightness needs, energy efficiency, and budget.
Q: Are all LCD panels made with the same type of glass?
A: No. Manufacturers use different types depending on application requirements such as strength, clarity, thickness, or environmental durability.
Q: Can I replace just the glass part if my screen cracks?
A: In some cases yes—if only the outer cover glass is damaged—but it depends on how the display is bonded internally. Professional repair or replacement is often required to restore full functionality without damaging internal components.


 2025-11-07
2025-11-07  11:50
11:50